AstronomicAL
An interactive dashboard for visualisation, integration and classification of data using Active Learning.
Cite this software
Description
AstronomicAL
An interactive dashboard for visualisation, integration and classification of data using Active Learning.
https://github.com/grant-m-s/AstronomicAL/assets/12834844/4724c341-2a96-446b-8cd0-fcb6ac9efef8
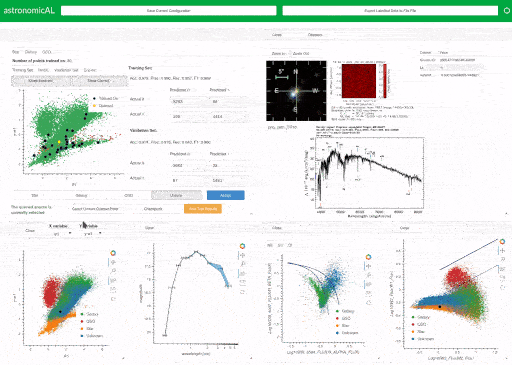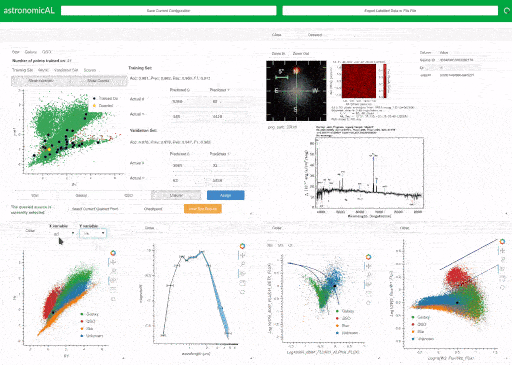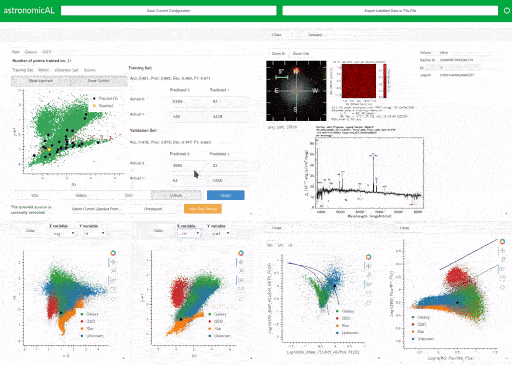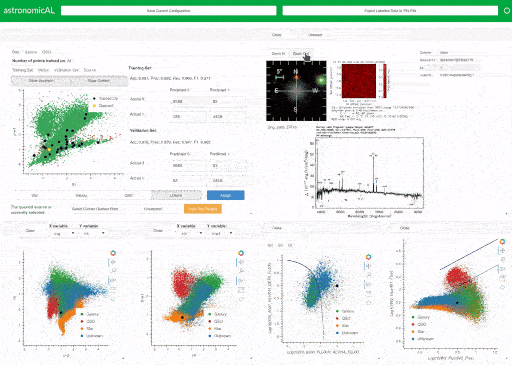
AstronomicAL is a human-in-the-loop interactive labelling and training dashboard that allows users to create reliable datasets and robust classifiers using active learning. The system enables users to visualise and integrate data from different sources and deal with incorrect or missing labels and imbalanced class sizes by using active learning to help the user focus on correcting the labels of a few key examples. Combining the use of the Panel, Bokeh, modAL and SciKit Learn packages, AstronomicAL enables researchers to take full advantage of the benefits of active learning: high accuracy models using just a fraction of the total data, without the requirement of being well versed in underlying libraries.

Statement of Need
Active learning (Settles, 2012) removes the requirement for large amounts of labelled training data whilst still producing high accuracy models. This is extremely important as with ever-growing datasets; it is becoming impossible to manually inspect and verify ground truth used to train machine learning systems. The reliability of the training data limits the performance of any supervised learning model, so consistent classifications become more problematic as data sizes increase. The problem is exacerbated when a dataset does not contain any labelled data, preventing supervised learning techniques entirely. AstronomicAL has been developed to tackle these issues head-on and provide a solution for any large scientific dataset.
It is common for active learning to query areas of high uncertainty; these are often in the boundaries between classes where the expert's knowledge is required. To facilitate this human-in-the-loop process, AstronomicAL provides users with the functionality to fully explore each data point chosen. This allows them to inject their domain expertise directly into the training process, ensuring that asigned labels are both accurate and reliable.
AstronomicAL has been extensively validated on astronomy datasets. These are highly representative of the issues that we anticipate will be found in other domains for which the tool is designed to be easily customisable. Such issues include the volume of data (millions of sources per survey), vastly imbalanced classes and ambiguous class definitions leading to inconsistent labelling. AstronomicAL has been developed to be sufficiently general for any tabular data and can be customised for any domain. For example, we provide the functionality for data fusion of catalogued data and online cutout services for astronomical datasets.
Using its modular and extensible design, researchers can quickly adapt AstronomicAL for their research to allow for domain-specific plots, novel query strategies, and improved models. Furthermore, there is no requirement to be well-versed in the underlying libraries that the software uses. This is due to large parts of the complexity being abstracted whilst allowing more experienced users to access full customisability.
As the software runs entirely locally on the user's system, AstronomicAL provides a private space to experiment whilst providing a public mechanism to share results. By sharing only the configuration file, users remain in charge of distributing their potentially sensitive data, enabling collaboration whilst respecting privacy.
Documentation
The documentation for AstronomicAL can be found here.
Installation
To install AstronomicAL and its dependencies, the user can clone the repository and from within the repo folder run pip install -r requirements.txt. . It is recommended that the user creates a virtual environment using tools such as Virtualenv or Conda, to prevent any conflicting package versions.
git clone https://github.com/grant-m-s/AstronomicAL.git
cd AstronomicAL
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda create --name astronomical --file requirements.txt python=3.8
conda activate astronomical
Quickstart Instructions
To begin using the software, run bokeh serve astronomicAL --show and your browser should automatically open to localhost:5006/astronomicAL
AstronomicAL provides both an example dataset and an example configuration file to allow you to jump right into the software and give it a test run.

To begin training you simply have to select Load Custom Configuration checkbox and select your config file. Here we have chosen to use the example_config.json file.
The Load Config Select option allows use to choose the extent to which to reload the configuration.
Contributing to AstronomicAL
Reporting Bugs
If you encounter a bug, you can directly report it in the issues section.
Please describe how to reproduce the bug and include as much information as possible that can be helpful for fixing it.
Are you able to fix a bug?
You can open a new pull request or include your suggested fix in the issue.
Submission of extensions
Have you created an extension that you want to share with the community?
Create a pull request describing your extension and how it can improve research for others.
Support and Feedback
We would love to hear your thoughts on AstronomicAL.
Are there any features that would improve the effectiveness and usability of AstronomicAL? Let us know!
Any feedback can be submitted as an issue.
Referencing the Package
Please remember to cite our software and user guide whenever relevant.
See the Citing page in the documentation for instructions about referencing and citing the astronomicAL software.